Перегляд архіву пʼятниця, 31 січня 2025
Daily bulletin on solar and geomagnetic activity from the SIDC
Випущено: 2025 Jan 31 1242 UTC
SIDC Forecast
Сонячні спалахи
M-class flares expected (probability >=50%)
Geomagnetism
Minor storm expected (A>=30 or K=5)
Сонячні протони
Quiet
| 10cm flux | Ap | |
|---|---|---|
| 31 Jan 2025 | 190 | 013 |
| 01 Feb 2025 | 193 | 016 |
| 02 Feb 2025 | 194 | 011 |
Solar Active Regions and flaring
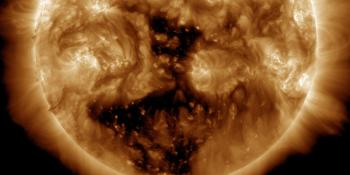
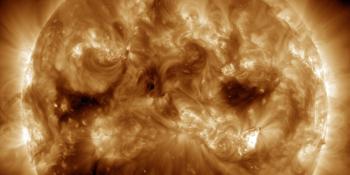
A total of 7 numbered sunspot groups were identified on the disk over the past 24 hours. Solar flaring activity was moderate over the past 24 hours, with one M-class flare identified. The largest flare was an M1.0 flare peaking on January 31 at 06:08 UTC, which was produced by SIDC Sunspot Group 388 (NOAA Active Region 3976). The most magnetically complex and largest region on the solar disk is SIDC Sunspot Group 388 (NOAA Active Region 3976), which has a Beta-Gamma-Delta magnetic configuration. This region also produced most of the flaring activity in the last 24 hours. SIDC Sunspot Group 390 (NOAA Active Region 3980) and SIDC Sunspot Group 391 (NOAA Active Region 3981) have rotated over the east limb onto the visible solar disk. Solar flaring activity is expected to be moderate over the next 24 hours, with M-class flares very likely and a small chance for X-class flares.
Корональні викиди маси
A Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) was observed at 16:12 UTC on January 30 in LASCO-C2 data, associated with a filament eruption in the southeast quadrant of the Sun. This CME is expected to arrive at Earth on February 03. A second CME observed in LASCO-C2 data around the same time, which is associated with SIDC Sunspot Group 388 (NOAA Active Region 3976) is expected to miss the Earth.
Корональні діри
Returning SIDC Coronal Hole 82 (equatorial coronal hole with a positive polarity) and returning SIDC Coronal Hole 60 (mid-latitude coronal hole with a positive polarity) both started to cross the central meridian on January 28 and are continuing to cross the central meridian.
Сонячний вітер
In the past 24 hours solar wind conditions at Earth were disturbed (enhanced magnetic fields and density), due to an ICME glancing blow, probably associated with a CME that left the Sun on January 28. The total interplanetary magnetic field started to increase, around 15:00 UTC on January 30, from 4 nT to a peak of 16 nT, with the Bz component reaching a minimum of -12 nT. The solar wind speed gradually increased from 290 km/s to 367 km/s. The phi-angle was mainly in the positive sector (directed away from the Sun) with periods in the negative sector. The solar wind conditions are expected to remain under the influence of the ICME and become more disturbed in the next 24 hours due to the anticipated high- speed-streams arrivals associated with two positive polarity coronal holes that started to cross the central meridian on January 28.
Geomagnetism
The geomagnetic conditions over the past 24 hours were globally and locally quiet to unsettled (Kp 1-3 & K BEL 1-3). Active to minor storm conditions are expected for the next 24 hours.
Proton flux levels
Over the past 24 hours, the greater than 10 MeV GOES proton flux was at background levels and is expected to remain so over the next days.
Electron fluxes at geostationary orbit
The greater than 2 MeV electron flux, as measured by the GOES-16 and GOES-18 satellites remained below the threshold level in the last 24 hours. The electron flux is expected to remain below the threshold in the coming 24 hours. The 24h electron fluence is presently at normal level, and it is expected to remain so in the next 24 hours.
Today's estimated international sunspot number (ISN): 142, based on 08 stations.Solar indices for 30 Jan 2025
| Wolf number Catania | 109 |
| 10cm solar flux | 184 |
| AK Chambon La Forêt | 011 |
| AK Wingst | 007 |
| Estimated Ap | 005 |
| Estimated international sunspot number | 105 - Based on 21 stations |
Noticeable events summary
| Day | Begin | Max | Кінець | Loc | Strength | OP | 10cm | Catania/NOAA | Radio burst types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31 | 0548 | 0610 | 0620 | ---- | M1.0 | --/---- | III/2 |
Provided by the Solar Influences Data analysis Center© - SIDC - Processed by SpaceWeatherLive
Весь час у UTC
Останні новини
Останні повідомлення з форума
Підтримайте SpaceWeatherLive.com!
Багато людей відвідують сайт SpaceWeatherLive, щоб слідкувати за сонячною та авроральною активністю, але зі збільшенням трафіку хостинг також стає дорожчим. Будь-ласка, подумайте про пожертву, якщо вам подобається SpaceWeatherLive, щоб ми могли і надалі підтримувати цей сайт і платити за хостинг!

Факти про космічну погоду
| Останній X-спалах | 2025/03/28 | X1.1 |
| Останній M-спалах | 2025/04/01 | M2.5 |
| Останній геомагнітний шторм | 2025/03/27 | Kp5 (G1) |
| Дні без сонячних плям | |
|---|---|
| Останній день без сонячних спалахів | 2022/06/08 |
| Середня кількість сонячних плям протягом місяця | |
|---|---|
| лютого 2025 | 154.6 +17.6 |
| квітня 2025 | 147 -7.6 |
| Останні 30 днів | 128.8 -21.8 |