Failed storm prediction, Next coronal hole
Thursday, 18 May 2017 13:22 UTC
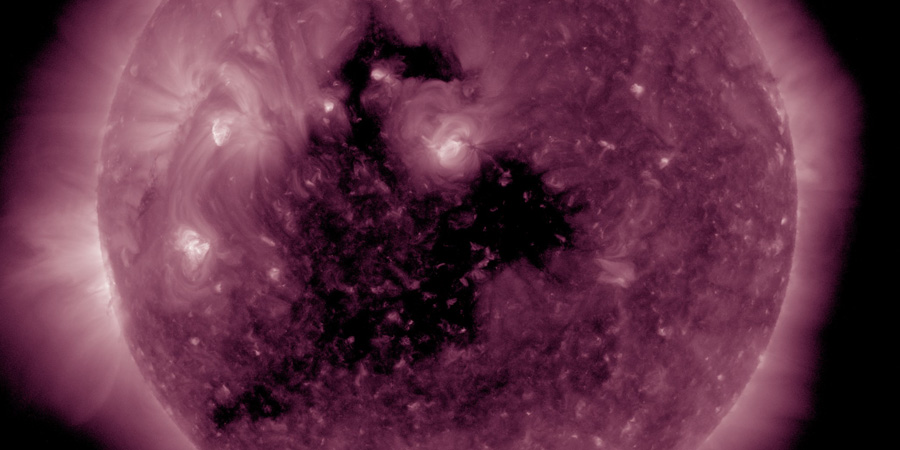
The NOAA SWPC had a moderate G2 geomagnetic storm watch in effect during the past few days but we unfortunately haven't even reached the minor G1 geomagnetic storm level. The G2 geomagnetic storm watch from the NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center was a result of a possible coronal mass ejection (CME) impact, something we indeed never mentioned on the site or on our social media pages. We did not believe this solar storm had an earth-bound component so choose to not mention it, a strategy that proved to be the right one. A minor G1 geomagnetic storm was however predicted due to a coronal hole solar wind stream but the stream was weaker than expected and only caused active geomagnetic conditions (Kp4) on 15 May. We are however getting another chance to reach geomagnetic storm levels thanks to yet another coronal hole.
A coronal hole is facing Earth. Enhanced solar wind could arrive in ~3 days - Follow live on https://t.co/T1Jkf6i4Cb pic.twitter.com/IHjk2f3PC2
— SpaceWeatherLive (@_SpaceWeather_) May 17, 2017
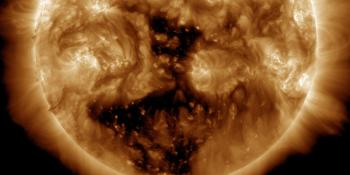
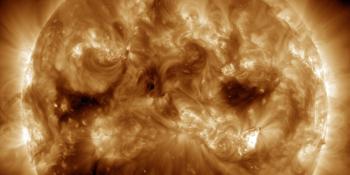
This coronal hole is also a coronal hole that has been around for a long time but a quick comparison with how this coronal hole looked like during the last rotation shows that it did not change all that much. In fact it might even have become slightly bigger.
That is excellent news as this coronal hole caused solar wind speeds up to 750km/s during the previous rotation and a lot of geomagnetic storming. The NOAA SWPC has a moderate G2 geomagnetic storm watch in effect for tomorrow evening (UTC) which could very well be possible considering the history of this coronal hole. Well worth to keep your eyes on the solar wind data starting tomorrow evening to see how this is going to develop. The moon is lit for about 50% so it shouldn't be a major problem. Especially for our southern hemisphere sky watchers this could be a very interesting events as their nights are becoming longer and longer but even middle latitude sky watchers in Europe and North America should be alert.
Thank you for reading this article! Did you have any trouble with the technical terms used in this article? Our help section is the place to be where you can find in-depth articles, a FAQ and a list with common abbreviations. Still puzzled? Just post on our forum where we will help you the best we can!
Latest news
Latest forum messages
More topicsSupport SpaceWeatherLive.com!
A lot of people come to SpaceWeatherLive to follow the Sun's activity or if there is aurora to be seen, but with more traffic comes higher server costs. Consider a donation if you enjoy SpaceWeatherLive so we can keep the website online!

Space weather facts
| Last X-flare | 2025/03/28 | X1.1 |
| Last M-flare | 2025/04/01 | M2.4 |
| Last geomagnetic storm | 2025/03/27 | Kp5 (G1) |
| Spotless days | |
|---|---|
| Last spotless day | 2022/06/08 |
| Monthly mean Sunspot Number | |
|---|---|
| February 2025 | 154.6 +17.6 |
| April 2025 | 147 -7.6 |
| Last 30 days | 128.8 -21.8 |