Viewing archive of Saturday, 18 February 2023
Daily bulletin on solar and geomagnetic activity from the SIDC
Issued: 2023 Feb 18 1236 UTC
SIDC Forecast
Solar flares
M-class flares expected (probability >=50%)
Geomagnetism
Minor storm expected (A>=30 or K=5)
Solar protons
Quiet
| 10cm flux | Ap | |
|---|---|---|
| 18 Feb 2023 | 160 | 011 |
| 19 Feb 2023 | 165 | 034 |
| 20 Feb 2023 | 168 | 016 |
Bulletin
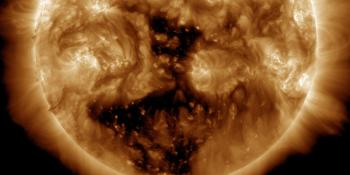
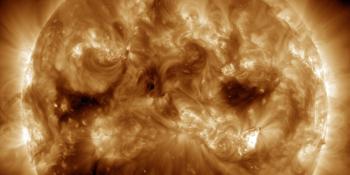
Solar flaring activity reached high levels over the past 24 hours. The largest flare was a X2.2 flare, with peak time 20:16 UTC on February 17, associated with NOAA AR 3229 in the north east of the solar disk. This event was associated with a dimming and EUV wave as well as a Type II radio signature. This region was responsible for much of the flaring activity. NOAA AR 3226 also produced low level flaring activity. NOAA AR3225 exhibited rapid growth over the period. A new region is also expected to rotate onto the disk over the south east limb. The remaining regions on the solar disk are all relatively simple and have not produced any significant flaring activity. The solar flaring activity is expected to be at moderate levels over the next 24 hours with C-class flares expected, M-class flares likely and a low probability for further X-class flares.
A halo Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) associated with the X2.2 flare was observed by STEREO-A/COR2 from 20:38 UT and in SOHO/LASCO-C2 data from 20:12 UT. The CME is directed to the north east and the bulk of the CME is not expected to be Earth directed. However, a glancing blow of the shock is predicted to impact Earth early on February 20. A second partial halo CME was observed in LASCO-C2 from 02:36UT February 18, directed to the south east. This is a back-sided eruption and is not expected to impact Earth.
The greater than 10 MeV proton flux was at nominal levels in the past 24 hours. There is a small chance of a proton event exceeding the 10pfu threshold, due to possible further high level flares. The greater than 2 MeV electron flux was below the 1000 pfu threshold and is expected to remain below this threshold over the next days. The 24h electron fluence was at nominal levels and is expected to be at nominal levels over the next 24 hours.
The Solar wind conditions reflected the waning influence of the high-speed stream.The solar wind speed decreased from 500 km/s to values around 400 km/s. The total interplanetary magnetic field fluctuated around 5nT. Bz had a minimum value of -5nT. The interplanetary magnetic field was predominantly in the positive sector (directed away from the Sun). The solar wind conditions are expected to become enhanced again from late on February 18, due to a combination of two predicted glancing blows from CMEs. From early on February 20, the shock associated with the halo CME of February 17 is also expected to arrive.
The geomagnetic conditions were at quiet to unsettled levels over the past 24 hours (local K-Bel 0-3 and NOAA Kp 0-2). Quiet conditions are expected for February 18 with active to minor (possibly major) storm conditions possible on February 19 and 20, due to the possible predicted CME arrivals.
Today's estimated international sunspot number (ISN): 123, based on 08 stations.Solar indices for 17 Feb 2023
| Wolf number Catania | 100 |
| 10cm solar flux | 343 |
| AK Chambon La Forêt | 010 |
| AK Wingst | 006 |
| Estimated Ap | 007 |
| Estimated international sunspot number | 093 - Based on 15 stations |
Noticeable events summary
| Day | Begin | Max | End | Loc | Strength | OP | 10cm | Catania/NOAA | Radio burst types |
|---|
Provided by the Solar Influences Data analysis Center© - SIDC - Processed by SpaceWeatherLive
All times in UTC
Latest news
Latest forum messages
Support SpaceWeatherLive.com!
A lot of people come to SpaceWeatherLive to follow the Sun's activity or if there is aurora to be seen, but with more traffic comes higher server costs. Consider a donation if you enjoy SpaceWeatherLive so we can keep the website online!

Space weather facts
| Last X-flare | 2025/03/28 | X1.1 |
| Last M-flare | 2025/04/01 | M5.6 |
| Last geomagnetic storm | 2025/03/27 | Kp5 (G1) |
| Spotless days | |
|---|---|
| Last spotless day | 2022/06/08 |
| Monthly mean Sunspot Number | |
|---|---|
| February 2025 | 154.6 +17.6 |
| Last 30 days | 128.5 -22.7 |