Viewing archive of Saturday, 1 February 2025
Daily bulletin on solar and geomagnetic activity from the SIDC
Issued: 2025 Feb 01 1234 UTC
SIDC Forecast
Solar flares
M-class flares expected (probability >=50%)
Geomagnetism
Minor storm expected (A>=30 or K=5)
Solar protons
Quiet
| 10cm flux | Ap | |
|---|---|---|
| 01 Feb 2025 | 217 | 019 |
| 02 Feb 2025 | 218 | 019 |
| 03 Feb 2025 | 217 | 016 |
Solar Active Regions and flaring
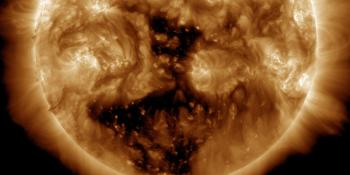
A total of 9 numbered sunspot groups were identified on the disk over the past 24 hours. Solar flaring activity was moderate over the past 24 hours, with 2 M-class flares identified. The largest flare was a M6.7 flare (SIDC Flare 3428) peaking on January 31 at 14:06 UTC, which was produced by SIDC Sunspot Group 360 (NOAA Active Regions 3947, 3978). The second largest flare was a M1.8 flare (SIDC Flare 3431) peaking on January 31 at 20:23 UTC and was produced by SIDC Sunspot Group 368 (NOAA Active Regions 3953, 3977). The most magnetically complex and largest region on the solar disk is SIDC Sunspot Group 388 (NOAA Active Region 3976), which has a Beta-Gamma-Delta magnetic configuration. This region also produced most of the flaring activity in the last 24 hours. SIDC Sunspot Group 360 (NOAA Active Region 3978) and SIDC Sunspot Group 368 (NOAA Active Region 3977) both have a Beta-Gamma magnetic configuration. Solar flaring activity is expected to be moderate over the next 24 hours, with M-class flares very likely and a small chance for X-class flares.
Coronal mass ejections
A Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) was observed at 14:24 UTC on January 3 in LASCO-C2 data, associated with a M6.7 flare (SIDC Flare 3428). This CME is expected to arrive at Earth on February 04.
Coronal holes
Returning SIDC Coronal Hole 82 (equatorial coronal hole with a positive polarity) and returning SIDC Coronal Hole 60 (mid-latitude coronal hole with a positive polarity) both started to cross the central meridian on January 28 and are continuing to cross the central meridian.
Solar wind
In the past 24 hours solar wind conditions at Earth were still disturbed, due to an ICME arrival on January 30 and the arrival of a high- speed stream (HSS), associated with SIDC Coronal Hole 82. The solar wind speed started to gradually increase, around 21:00 UTC on January 31 from 360 km/s to 585 km/s. The total interplanetary magnetic ranged from 6 nT to a peak of 19 nT, with the Bz component reaching a minimum of -17 nT. The phi-angle was in the negative sector (directed towards the Sun) until 22:15 UTC on January 31 when it switched to the positive sector. The solar wind conditions are expected to remain under the influence of the ICME and HSS and remain disturbed in the next 24 hours.
Geomagnetism
The geomagnetic conditions over the past 24 hours reached active conditions globally (Kp 4) and locally were quiet to unsettled (K BEL 1-3). Active to minor storm conditions are expected for the next 24 hours.
Proton flux levels
Over the past 24 hours, the greater than 10 MeV GOES proton flux was at background levels and is expected to remain so over the next days.
Electron fluxes at geostationary orbit
The greater than 2 MeV electron flux, as measured by the GOES-16 and GOES-18 satellites remained below the threshold level in the last 24 hours. The electron flux is expected to remain below the threshold in the coming 24 hours. The 24h electron fluence is presently at normal level, and it is expected to remain so in the next 24 hours.
Today's estimated international sunspot number (ISN): 144, based on 10 stations.Solar indices for 31 Jan 2025
| Wolf number Catania | 151 |
| 10cm solar flux | 207 |
| AK Chambon La Forêt | 018 |
| AK Wingst | 008 |
| Estimated Ap | 008 |
| Estimated international sunspot number | 146 - Based on 23 stations |
Noticeable events summary
| Day | Begin | Max | End | Loc | Strength | OP | 10cm | Catania/NOAA | Radio burst types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31 | 1340 | 1406 | 1425 | N11E43 | M6.7 | 1N | 22/3978 | VI/2 | |
| 31 | 2014 | 2023 | 2028 | N23E28 | M1.8 | SF | 21/3977 | III/3 |
Provided by the Solar Influences Data analysis Center© - SIDC - Processed by SpaceWeatherLive
All times in UTC
Latest news
Latest forum messages
Support SpaceWeatherLive.com!
A lot of people come to SpaceWeatherLive to follow the Sun's activity or if there is aurora to be seen, but with more traffic comes higher server costs. Consider a donation if you enjoy SpaceWeatherLive so we can keep the website online!

Space weather facts
| Last X-flare | 2025/03/28 | X1.1 |
| Last M-flare | 2025/04/22 | M1.3 |
| Last geomagnetic storm | 2025/04/21 | Kp5+ (G1) |
| Spotless days | |
|---|---|
| Last spotless day | 2022/06/08 |
| Monthly mean Sunspot Number | |
|---|---|
| March 2025 | 134.2 -20.4 |
| April 2025 | 121.5 -12.7 |
| Last 30 days | 114.6 -22.2 |